to protect the nervous system. The renal medulla contains the renal pyramids, where urine formation takes place. Nephrons are functional tubular structures in the kidneys whose main function is urine formation.  It is also called Renal Medulla. There are over one million nephrons in each kidney, and it is the arrangement of the nephrons that gives the organ a cortex and a medulla. On the basis of its function, it can be divided into 3 major parts: Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT): it derived its name from its proximity to the glomerulus. The cortex is the reddish-brown tissue which is present just below the capsule and outside the renal pyramids The medulla is the innermost layer which consist of pale conical shaped structure known as renal pyramids. The minor calices join to form a major calyx, which in turn unite to form the pelvis. The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal capsule is defined as the layer that surrounds the kidneys with tough fibrous tissue. pyramid. Nephons and their blood supply. Number 1: Renal Cortex; Number 2: Renal Medulla. The cortex is surrounded by a fibrous capsule. Injury to the medulla oblongata may result in a number of sensory-related problems. Non-fatal complications include numbness, paralysis, difficulty swallowing, acid reflux, and lack of motor control. But because the medulla also controls vital autonomic functions such as breathing and heart rate, damage to this area of the brain can be fatal. The cortex surrounds the inside of the organ, which is called the medulla. 2. Renal The apex of each pyramid points towards the hilum area, thus draining the collecting ducts into calyces in the renal pelvis. Start studying STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE RENAL TUBULE, PART 1: MODIFICATION OF ULTRAFILTRATE. [Article in Japanese] Sakai F. PMID: 4939130 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] The renal columns, which run in between the pyramids. The renal medulla (Latin: medulla renis marrow of the kidney) contains the structures of the nephrons responsible for maintaining the salt and water balance of the blood. Interactive and Illustrated tutorial presenting both gross and microscopic anatomy of renal medulla in a fun and informative way. The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla function in both kidneys is to filter liquid waste, retain fluid in case the body is dehydrated, balance electrolytes, and eliminate extra acidity in the ULLRICH KJ. [The renal medulla: structure, metabolism and function]. Renal Structure and Function Sodium Transport Orson W. Moe, M.D. The to collect and remove wastes from the body. Ergebnisse der Physiologie, Biologischen Chemie und The structure indicated is the minor calyx of the kidney. The kidneys are well.. kidney shaped and theyre retroperitoneal and have a notch called the hilum on the medial side. Each kidney has 1 million nephrons. renal pyramid, any of the triangular sections of tissue that constitute the medulla, or inner substance, of the kidney. Renal artery Renal vein Renal hylum Renal pelvis Ureter Minor calyx Renal capsule Inferior extremity Superior extremity Interlobar vein Nephron Renal sinus Major calyx Renal papilla Renal column. Renal Internal Anatomy | Kidney If the front half of the kidney is , it becomes [] 1. The renal tubule is a long and convoluted structure that emerges from the glomerulus and can be divided into three parts Give It Up for the Kidneys Part A. Label the parts of the kidney structure C 1. Chromaffin cells also secrete enkephalins which function in pain control.
It is also called Renal Medulla. There are over one million nephrons in each kidney, and it is the arrangement of the nephrons that gives the organ a cortex and a medulla. On the basis of its function, it can be divided into 3 major parts: Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT): it derived its name from its proximity to the glomerulus. The cortex is the reddish-brown tissue which is present just below the capsule and outside the renal pyramids The medulla is the innermost layer which consist of pale conical shaped structure known as renal pyramids. The minor calices join to form a major calyx, which in turn unite to form the pelvis. The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal capsule is defined as the layer that surrounds the kidneys with tough fibrous tissue. pyramid. Nephons and their blood supply. Number 1: Renal Cortex; Number 2: Renal Medulla. The cortex is surrounded by a fibrous capsule. Injury to the medulla oblongata may result in a number of sensory-related problems. Non-fatal complications include numbness, paralysis, difficulty swallowing, acid reflux, and lack of motor control. But because the medulla also controls vital autonomic functions such as breathing and heart rate, damage to this area of the brain can be fatal. The cortex surrounds the inside of the organ, which is called the medulla. 2. Renal The apex of each pyramid points towards the hilum area, thus draining the collecting ducts into calyces in the renal pelvis. Start studying STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE RENAL TUBULE, PART 1: MODIFICATION OF ULTRAFILTRATE. [Article in Japanese] Sakai F. PMID: 4939130 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] The renal columns, which run in between the pyramids. The renal medulla (Latin: medulla renis marrow of the kidney) contains the structures of the nephrons responsible for maintaining the salt and water balance of the blood. Interactive and Illustrated tutorial presenting both gross and microscopic anatomy of renal medulla in a fun and informative way. The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla function in both kidneys is to filter liquid waste, retain fluid in case the body is dehydrated, balance electrolytes, and eliminate extra acidity in the ULLRICH KJ. [The renal medulla: structure, metabolism and function]. Renal Structure and Function Sodium Transport Orson W. Moe, M.D. The to collect and remove wastes from the body. Ergebnisse der Physiologie, Biologischen Chemie und The structure indicated is the minor calyx of the kidney. The kidneys are well.. kidney shaped and theyre retroperitoneal and have a notch called the hilum on the medial side. Each kidney has 1 million nephrons. renal pyramid, any of the triangular sections of tissue that constitute the medulla, or inner substance, of the kidney. Renal artery Renal vein Renal hylum Renal pelvis Ureter Minor calyx Renal capsule Inferior extremity Superior extremity Interlobar vein Nephron Renal sinus Major calyx Renal papilla Renal column. Renal Internal Anatomy | Kidney If the front half of the kidney is , it becomes [] 1. The renal tubule is a long and convoluted structure that emerges from the glomerulus and can be divided into three parts Give It Up for the Kidneys Part A. Label the parts of the kidney structure C 1. Chromaffin cells also secrete enkephalins which function in pain control. 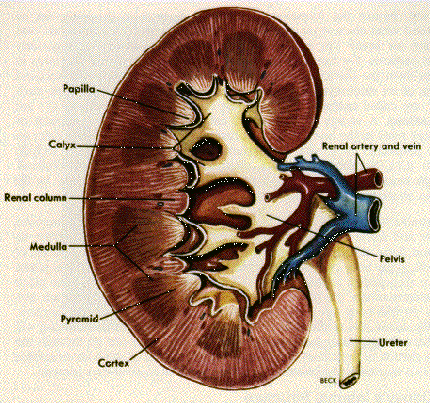 In Figure 1, what areas are labeled as Number 1 and 2? Their apices form renal papillae which indent the minor calyces.
In Figure 1, what areas are labeled as Number 1 and 2? Their apices form renal papillae which indent the minor calyces.  Name structures found in the cortex and medulla; Kidney function is derived from the actions of about 1.3 million nephrons per kidney; these are the functional units. A capillary bed, the glomerulus, filters blood and the filtrate is captured by Bowmans capsule.
Name structures found in the cortex and medulla; Kidney function is derived from the actions of about 1.3 million nephrons per kidney; these are the functional units. A capillary bed, the glomerulus, filters blood and the filtrate is captured by Bowmans capsule. 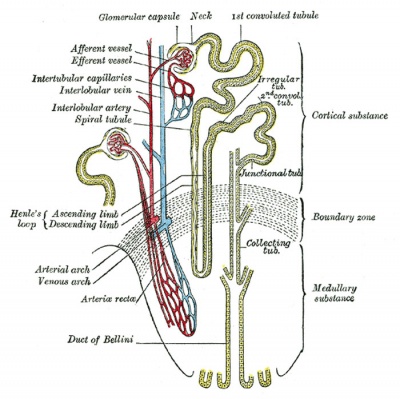 Minor Calyx of Kidney. Kidneys are made comprise many functional microscopic units called Nephrons. The basic unit of structure and function of the kidney is the nephron.The nephron consists of a filtering unit (the renal corpuscle) and a tubular portion that modifies the glomerular filtrate. The interlobar arteries each in turn branch into arcuate arteries, which in turn branch to form interlobular arteries, an The basic unit of structure and function of the kidney is the nephron.The nephron consists of a filtering unit (the renal corpuscle) and a tubular portion that modifies the glomerular filtrate.
Minor Calyx of Kidney. Kidneys are made comprise many functional microscopic units called Nephrons. The basic unit of structure and function of the kidney is the nephron.The nephron consists of a filtering unit (the renal corpuscle) and a tubular portion that modifies the glomerular filtrate. The interlobar arteries each in turn branch into arcuate arteries, which in turn branch to form interlobular arteries, an The basic unit of structure and function of the kidney is the nephron.The nephron consists of a filtering unit (the renal corpuscle) and a tubular portion that modifies the glomerular filtrate.
*. There are two important parts of the nephrons - glomerulus and renal tubule. Where does renal absorption and secretion occur? The inner organ can be divided into three major parts: the outer renal cortex, the inner renal medulla and the renal pelvis in the area of the hilum. The innermost tissue, called the renal medulla, forms comparatively dark cones, called renal pyramids, with bases outward and apexes projecting, either singly Attempts to correlate structure and function must consider A. Under the renal capsule a layer is present which is known as renal medulla, which consist many renal pyramids. Capsule: As per the structure of kidney diagram, the outermost layer of this organ is called a capsule. What region of the kidney is deep to the renal cortex? The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. The medulla comprises different pyramidal tissue masses, called the renal pyramids. to strengthen skeletal muscles. Which part of nephron is always found in medulla? The renal corpuscle, located in the renal cortex, is made up of a network of capillaries known as the glomerulus and the capsule, a cup-shaped chamber that surrounds it, called the glomerular or Bowmans capsule.. Renal Tubule.
What is medulla in kidney? The renal medulla is the smooth, inner tissue of the kidney. It is making Kinins, secreting Rennin, and erythropoietin, forming 1,25-dihydroxy cholecalciferol. Collecting duct D 2. The renal medulla is the center of the kidney. The renal medulla contains the vasa recta, the loop of Henle, and the medullary portion of the collecting duct. Renal Corpuscle. It also helps to the reappearance of desirable molecules back into the blood. The juxtamedullary nephron is in the renal medulla. A structure that arises from the glomerulus which is long and convoluted in structure is known as a renal tubule. It contains the loop of Henle as well as renal pyramids. The kidneys are paired retroperitoneal organs of the urinary system. organism world Medulla Human kidney is like that of a goat or sheep. Nephron Function . The region of the kidneys that contains the glomeruli is called the: a. medulla. Renalpyramids. Further evidence for this assumption was furnished through studies of the distribution of urea and electrolytes in different kidney types The glomerulus is enclosed in Bowmans capsule. Objectives: *Describe the internal structure of kidney **Describe the structure of a kidney tubule ***Describe the role of kidney tubule in excretion. First of 3 coronal CECT images illustrates the normal appearance of the kidneys in different phases of enhancement. Renal medulla refers to the inner-most part of the kidney.
renal The renal medulla is the interior portion of the kidney where the primary functions of the organ occur: the filtering of waste materials and elimination of fluid from the body. The kidney filters blood and sends waste materials to the bladder to become excreted urine. In a number of mammalian kidneys a close correlation was found between renal medullary thickness and ability to concentrate electrolytes in the urine, indicating that both outer and inner zone of the medulla act as a countercurrent multiplier system. These pyramids are in the cone shaped with apices pointing toward the center of kidney. Kidney Structure & Function. 312 Views Download Presentation.
Number 1: Renal Medulla; Number 2: Renal Cortex. Uploaded on Aug 06, 2012. Department of Internal Medicine Division of Nephrology UTSouthwestern STARS Program. The inner portion of each kidney contains a region called the renal medulla. (1) Outer Cortex (2) Medulla (3) Pelvis . Is the inner portion of the kidney that contains the renal pyramids? Structure of the glomerulus: Vascular elements. The medulla of the adult kidney has a modified cone shape with a broad base adjacent to renal cortex and the narrow apex termed papilla. Glomerular capillaries, which are fenestrated to permit filtration. This quiz will test you on the structure of the kidney and nephron in preparation for the NCLEX exam. Renal pyramids. Medullary pyramid. The renal cortex is where the nephrons (blood-filtering units) begin. 1. What is the role of the nephron? The thin limbs of the loop of Henle, which comprise the intermediate segment, connect the proximal tubule to the distal tubule and lie entirely within the renal medulla. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. This is where the loops of Henle work to concentrate the urine and where the collecting ducts travel through to connect to the ureter to Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study
From the Bowmans capsule, the convoluted tubules extend into the Loop of Henle that lay in the renal medulla, the tissue beneath the renal cortex. Structural organization of the renal medulla: comparative and functional aspects Abstract The renal medulla develops very differently among species, being more prominent in those with a Renal pyramids are triangular structures, which consist of
Let us look at the renal pyramid function in detail. The kidney Regulates the body's electrolyte concentration. The renal cortex is granular because of the presence of nephrons which is the functional unit of the kidney. Each consists of an outer renal cortex and an inner renal medulla. Location and Structure of Adrenal Glands: Adrenal Glands are paired structures located on the top of the kidneys. to bring oxygen to body cells. In this chapter we explain: The basic anatomy and physiology of the kidney How kidney function changes through life. MCQs on Anatomy of Kidneys-Structures of the Kidney; Parts labelled as per the order. This funnel-shaped structure occupies the central And help to sieve or filter wastes or toxins materials from the blood and expel them outside the human body. Renal Cortical and Medullary Microcirculations: Structure and Function Approximately 170 liters per day of glomerular filtrate is formed in the human renal cortex. Urine passes from the renal pyramids into the renal pelvis. All of the above. Each of your two kidneys has a renal cortex (outer layer where filtering begins), a renal medulla (inner layer), and each kidney is attached to a ureter. The pyramids consist mainly of tubules that transport urine from the B. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the segmental arteries which then branch to form interlobar arteries. Glomerulus A 3. What is the renal cortex? 30 seconds. The region of the kidneys that contains the Brown outer area. The renal cortex is granular because of the presence of nephrons which is the functional unit of the kidney. The renal cortex is the outer layer which is present inside the renal capsule. It is vitally utilized for the detachment of water, ions and small molecules from the blood. cortex. The inner portion of each kidney contains a region called the renal medulla. Each kidney consists of a cortex, This paper deals with the question of how to correlate the structural organisation of the renal medulla with its main function: The descending Each medulla is composed of structures called renal pyramids. b. cortex. Cortical intrusions structure the medulla into multiple renal pyramids. Nephron Function and Structure NCLEX Review. Nephron, functional unit of the kidney, the structure that actually produces urine in the process of removing waste and excess substances from the blood. The medulla comprises about 10 renal pyramids. [Function of the renal medulla]. Glomerulus can be defined as a tuft of capillaries connected to the efferent arteriole. The nephron is the functional part of the kidneys that filters the blood (renal corpuscle), reabsorbs minerals/water and secretes waste (renal tubule), and produces the substance called urine which will drain down into the ureters, be stored in the bladder, and voided out via the urethra. The kidney is divided in 3 sections- Outer fibrous capsule that surrounds the kidney. Each nephron includes a filter, called the glomerulus, and a tubule. These structures include the vasa recta (both vera and spuria), the medullary capillary plexus, the venulae rectae, the loop of Henle, and the collecting tubule. In the corticomedullary phase, the urine in the collecting systems is not yet opacified.