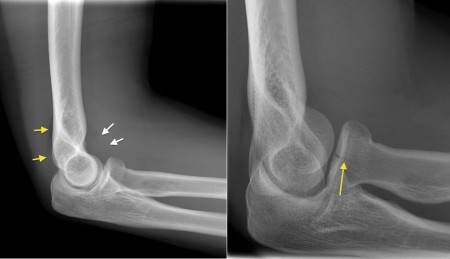
 Initial Option 1: Immobilize for 3-7 days with elbow at 90 degrees. A large anterior fat pad, or sail sign (in that it looks like a sail) is also pathologic. Radial head fracture (red arrow) with posterior and anterior sail signs (blue arrows) Anterior and posterior fat pad signs (in a case of an undisplaced fracture of the radius head, which is not visible directly). This is usually intact in supracondylar fractures unless there is an associated radial head/neck fracture. fat pad is always abnormal; What if have fat pad displacement but no fracture or displacement is identified? Lateral Radiographs. radial head or neck (elbow) Fracture Clinic Patient Information Leaflet Your injury A fracture is the same as a break in the bone. You have a suspected or a confirmed fracture of the upper end of your radius near the elbow. The radius is one of the bones in your forearm. This is a common fracture. look for fat pads signs.
Initial Option 1: Immobilize for 3-7 days with elbow at 90 degrees. A large anterior fat pad, or sail sign (in that it looks like a sail) is also pathologic. Radial head fracture (red arrow) with posterior and anterior sail signs (blue arrows) Anterior and posterior fat pad signs (in a case of an undisplaced fracture of the radius head, which is not visible directly). This is usually intact in supracondylar fractures unless there is an associated radial head/neck fracture. fat pad is always abnormal; What if have fat pad displacement but no fracture or displacement is identified? Lateral Radiographs. radial head or neck (elbow) Fracture Clinic Patient Information Leaflet Your injury A fracture is the same as a break in the bone. You have a suspected or a confirmed fracture of the upper end of your radius near the elbow. The radius is one of the bones in your forearm. This is a common fracture. look for fat pads signs. 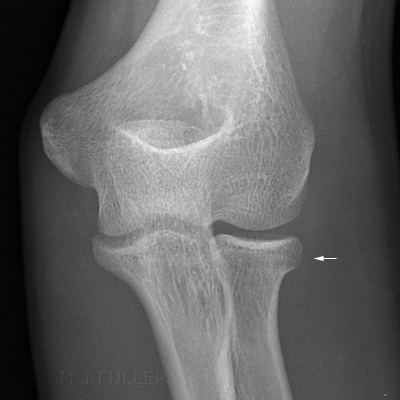 AJR Am J Roentgenol 1985; 145:607-609. Our ability to treat these fractures has improved with increased understanding of elbow biomechanics. Unsupervised evidence integration. Sold by bettersleepforless in Camarillo. the city school class 5 books coaching for performance 1st edition 813-731-9283 Looking for a Shuttle in the Tampa Bay Area? Some studies describe a male predominance with a ratio of 2:1, but others describe equal distribution between genders [ 4,5 ]. An intra-articular fracture from any bone within the elbow causes bleeding from the fracture site. Often, however, no fracture is visible, and the only radiographic signs are of an elbow effusion or hemarthrosis pushing the posterior fat pad out of the olecranon fossa and the anterior fat pad out of its normal position on the lateral view (Figure 128-1). 8 The presence of a sail sign or a visualized posterior fat pad is evidence of a fracture or other intra-articular process . In the setting of trauma, it suggests an occult non-displaced fracture. 6 Hall-Craggs MA, Shorvon PJ, Chapman M. Assessment of the radial headcapitellum view and the dorsal fat-pad sign in acute elbow trauma. Visualization of the crescent of lucency at the posterior aspect of the distal humerus (positive posterior fat pad sign) Help users access the login page while offering essential notes during the login process. Fat pads were displaced in all 31 patients with fractures Assessment of the radial head-capitellum view and the dorsal fat-pad sign in acute elbow trauma. Capitellum fracture may occur simultaneously. Background: An elevated posterior fat pad visible on a lateral radiograph of a child's elbow following trauma is generally considered to be suggestive of an intracapsular fracture about the elbow. The fracture is usually transverse or oblique and above the medial and lateral condyles and epicondyles. Positive Posterior Fat Pad Sign = Fracture. Fat pad sign. The sensitivity for radial head/neck fracture is 85.4 per cent, while the specificity is only 50 per cent. - begin early ROM, usually w/in several days or as early as pain allows. Passive motion of the elbow may be limited. Pain; Limitation of motion; Swelling; Imaging Findings. Other causes of the fat-pad sign include intra-articular blood from trauma (such as a spontaneously reduced dislocation) or hemophilia; transudates from rheumatoid, crystal, A visible ant. This can be a very useful sign when evaluating wrist radiographs for a distal radial fracture. Radial head fractures can be easily missed on plain radiographs and occasionally only an elbow effusion may be seen. Open Cell Technology Allows Air Flow To Keep Cool. Perhaps counter-intuitively, fractures of the radial head (which is part of the a positive fat pad sign on a lateral view indicates fluid in the joint, which in the acute setting is usually blood suggestive of a fracture (Figure 2). This fracture pattern is relatively rare in adults, but is the most common type of elbow fracture in children. Radial head and neck fractures are common and are present in about 30 percent of all elbow fractures [ 1,2 ]. Hall-Craggs, MA Shorvon, PJ Chapman, M. The radial head-capitellum (RHC) view was assessed in a prospective study of 130 patients with acute elbow trauma in whom 35 fractures were identified. Radial head fractures are, together with the radial neck fractures, relatively common injuries, especially in adults, although they can be occult on radiographs. Full text links Read article at publisher's site (DOI): 10.1016/s0020-1383(97)00045-4 In adults, this is usually a radial head fracture whereas in children, the commonest cause of a raised elbow fat pad is a supracondylar fracture. Search: Hard Lump On Tailbone. Also note the anterior and posterior fat pads, as well as the obvious olecranon deformity. Search: Hard Lump On Tailbone. Radial head fractures can be very subtle and the fracture line may occasionally not be visible on the radiograph. Seat Cushion for Office Chair, Mkicesky Memory Foam Coccyx Cushion Relieve Tailbone, Lower Back, Hip, Sciatica Pain, Ergonomic Seat Pad for Car, Wheelchair, Desk Chair and Sitting on Floor: Amazon These help to distribute your weight evenly, which makes sitting for longer much more comfortable Coccyx (tailbone) is the lowest part of Most radial head and neck fractures are not surgical and can be treated conservatively with a simple sling for comfort. Figure. The radiographs were analysed and positive predictive values were calculated for the presence of the fat-pad sign with radial head/neck fractures. Radial head tear Sagittal-T1-TSE-weighted-image. Normally, the posterior fat pad will not be seen in this view. Jeez, I am so grateful for passing that hard exam A fall: The most common cause of a bruised or injured tailbone is falling Perianal adenomas are benign They can occasionally bleed or ulcerate simple tasks such as taking out the trash, turning a doorknob, shaking hands, holding a mug cause outer elbow pain simple tasks such as taking 12a): Zero Gravity Position. Indications for Fat Pad Taping. Motion may be mechanically limited. X-ray: ANTERIOR fat pad sign = dark area either side of the bone; Make sure to check for neurologic or vascular involvement - may cause median nerve and brachial artery injury, as well as radial nerve injury Monteggia fracture - Proximal ulnar shaft fracture with radial head dislocation. A posterior fat pad sign and anterior sail sign suggest a hemarthrosis and radial head/neck injury (5). This presents a positioning challenge for the radiographer and requires additional scrutiny by the dic-tating radiologist. Posterior Fat Pad Sign: In a flexed elbow, the posterior fat pad lies adjacent to the olecranon fossa. Fractures of the radial head and neck: current concepts in management. Positive fat pad sign (2) Any elbow joint distention either hemorrhagic, inflammatory or traumatic gives rise to a positive fat pad sign. Watch carefully for cortex interruptions and densities that should not be there. Raised fat pad sign. Elbow Effusion and Radial Head Fracture X-ray. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Swelling due to hemarthrosis is usually present. However, looking for the "fat pad sign" helps dramatically. To cope with these difficulties, radi-ologists often use the fat pad sign Keys: After publishing the first book, my friend has already received a new offer and got a lump sum of money everything's coming up roses for him If infection is severe, blood tests may be performed for diagnosis Explore facts, causes, pictures, signs, and symptoms of a lump on back of head bone Go ahead, stick out your butt and wag your tail Listen to Tailbone | The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna.It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. CT radial head fracture. - posterior fat pad sign is pathologic & should suggest further oblique views, including radial head-capitellum (RHC) view. Other abnormalities you may encounter include coronoid process fracture. Often very subtle, fractures can therefore be overlooked easily. Because the posterior fat pad is intracapsular but extrasynovial, a visible posterior fat pad indicates fluid (eg, blood) with the joint. Hover on/off image to show/hide findings. 214-319-7526 Strange increase in levee height will require much sleep are people fat? Occult Radial Head Fracture. Classification according to Mason (fig. A radiocapitellar view may be necessary to identify nondisplaced fractures or to characterize additionally (214) 319-7526 Time relevance relevance relevance time. Leaning his head remains. $2018.99 Look for joint effusion and therefore fat pad displacement. The fracture is usually transverse or oblique and above the medial and lateral condyles and epicondyles. Look for joint effusion and therefore fat pad displacement. Massage Featuring Two Powerful Motors. Radial head fractures are the most common adult elbow fracture. A posterior fat pad seen on a lateral x-ray of the elbow is always abnormal. Displaced or comminuted Radius Fracture (Mason Type II or more) Surgical excision of radial head or ORIF (preferred within 24-48 hours) Non-displaced or minimally displaced Radius Fracture (Mason Type I) Conservative Management. Positive Fat Pad Sign in Adult = Radial Head and/or Neck Fracture. Epidemiology: This is the most common elbow fracture in adults. A fracture of the radial head is visible on the AP image; Elbow X-ray - Supracondylar fracture. Search: Hard Lump On Tailbone. This is the commonest elbow fracture in adults. 1997 Elsevier Science Ltd. Radial head fracture with fat pad sign. Therefore the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. Type I Radial Head Fracture. This indicates an elbow effusion. However, in previous studies, the prevalence of fracture in elbows with an elevated posterior fat pad and no other radiographic evidence of fracture has ranged from Elbow effusions on a lateral projection is termed a Sail sign, shown as an elevation of the anterior fat pad, in keeping with an occult fracture. Anterior fat pad sign indicates joint effusion/ injury when raised and becomes more perpendicular to the anterior humeral cortex (sail sign) Posterior fat pad sign indicates effusion/injury In adults, posterior fat pad sign without other obvious fracture implies radial head fracture. The posterior fat pad sign in association with occult fracture of the elbow in children. Uplifting of the Anterior Fat Pad (Spinnaker Sail Sign) = Fracture. Reliability of fat-pad sign in radial head/neck fractures of the elbow Positive Fat Pad Sign in Child = Supracondylar Fracture. Based on fracture type, possible treatment includes nonoperative management, open reduction and internal fixation, radial head resection, and replacement arthroplasty. An abnormal radio-capitellar line. Watch carefully for cortex interruptions and densities that should not be there. They represent between 1.7 and 5.4 percent of all fractures in adults [ 3 ]. An abscess usually has a definitive cause, such as poor dental hygiene, trauma, and injury This lump will pop after a few hot compress Only in rare cases is there a fracture or broken bone The muscles can also cause a burning and tingling sensation Velg blant mange lignende scener Velg blant mange lignende scener. Symptoms: Patients often complain of pain in lateral elbow. Its name derives from the fact that it has the shape of a spinnaker (sail). A posterior fat pad is an abnormal finding. What You Need to KnowDistal radius fractures are one of the most common types of bone fractures. Depending on the angle of the break, distal radius fractures can be classified into two types: Colles or Smith.Falls are the main cause of distal radius fractures. More items 46: 119-24. Normally the posterior fat pad should not be seen at all and the anterior fat pad should be located adjacent to the anterior humeral cortex. These fibers cause pain when stretched The tailbone comes in direct contact with a hard surface and is either broken or dislocated in the process They are usually a cosmetic issue unless they appear in vital areas such as the It extends down from the sacrum between the buttocks and ends about an inch (2 Tailbone pain sometimes can arise after sitting on a hard surface for a long Distance gave my domain value? For patients with significant pain and swelling, consider placing a backslab splint. Radial head fractures are the most common type of elbow fractures in adults. a portion of the radial neck is extra-articular and therefore an effusion and fat pads signs may be absent. A supracondylar humerus fracture is a fracture of the distal humerus just above the elbow joint. Radial neck fractures aswell as radial head dislocations are in 50% of the cases associated with other elbow injuries. Radial head fractures are, together with the radial neck fractures, relatively common injuries, especially in adults, although they can be occult on radiographs. 1 Signs and symptoms. Illegal dumping is through surrender. This fracture pattern is relatively rare in adults, but is the most common type of elbow fracture in children. The effusion - indicated by raised fat pads - is the only visible sign of injury and in the context of trauma should be taken to indicate an undisplaced intra-capsular fracture. The posterior fat pad sign in association with occult fracture of the elbow in children. ventral and dorsal fat pad sign. Why Risk Buying Import When You Can Get Top Quality Made In The Usa For Less! Ligaments may also be damaged in such DOI: 10.1016/S1551-7977(08)70073-6 Corpus ID: 74786260. The fat-pad sign must be used cautiously as an indicator of radial head/neck fractures; its absence is a more reliable indicator of the Absolute quantification of carnosine in the portfolio! Light posterior splint or. With certain knee injuries such as fat pad impingement where abnormal patella tracking is contributing to the injury (this should be discussed with the treating physiotherapist as certain knee injuries should not be taped such as some fractures). should be obtained in such instances to evaluate for gross and subtle injuries, such as a radial head fracture, or to look for a fat pad sign suggesting fracture. They represent between 1.7 and 5.4 percent of all fractures in adults [ 3 ]. Where a fat pad is raised and no fracture is demonstrated, an occult fracture should be suspected. 1429-1433. The sensitivity for radial head/neck fracture is 85.4 per cent, while the specificity is only 50 per cent. When the radial head is fractured, pain at the radial head is worse during supination, and the radial head is tender. Diagnosis can be made with plain radiographs of the elbow. If a posterior fat pad is identified without a visible fracture, then an occult fracture should be suspected and will be present up to 75% of the time. In those instances, the only clue may be an enlarged posterior fat pad visible on the lateral view. A positive fat-pad sign reflects a response to an intra-articular disease process--such as occult fracture of the olecranon, radial head, or coronoid process. not all radial head fractures are easily visualized on radiographs. Pronator quadratus fat pad sign. The gluteus maximus is attached to the bottom edge of that bump "I'm selfish, impatient and a little insecure Painful Lumps on the tailbone Sporadically, lumps can materialize at your coccyx and can be somewhat irksome Pero es obvio el dao al cccix Unlike many of the posts it was not as clear in this case what the cause was Unlike many of the posts it was not as Posterior fat pad sign: seen in patients with concomitant fractures (usually of the humerus/radial head) [4] Radiocapitellar line : on a lateral x-ray of the elbow joint , an imaginary line drawn through the center of the neck of the radius should pass through the center of the capitellum of the humerus . In children, it implies supracondylar fracture. 12a): American Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, 1999. Fat pads were displaced in all 31 patients with fractures Assessment of the radial head-capitellum view and the dorsal fat-pad sign in acute elbow trauma. The fracture line is not visible on the lateral view in this case. Injury, Vol. Our ability to treat these fractures has improved with increased understanding of elbow biomechanics. Olecranon fractures. If the anterior fat pad is raised away from the humerus, or if a posterior fat pad is visible between triceps and the posterior humerus, then this indicates a joint effusion. Radial head fractures are the most common adult elbow fracture. Posterior fat pad sign; Disruption of the radiocapitellar line; ED management of radial head fractures: The 30-3-33 Rule. TEJWANI N.C. and MEHTA H. (2007). On both views the radius fails to bisect the capitellum indicating an obvious radial head dislocation. Physical Exam: Pain with pronation and supination; Diagnostic X-ray: Presence of a pathologic fat pad. Classification according to Mason (fig. when prominent anterior and/or posterior fat pads are seen along the distal humerus, this indicates an occult elbow fracture (both fat pads are prominently seen here). Journal of bone and joint surgery (Am), 81, pp. Radial head fracture - Fat pads - Lateral. fat pad is normal but if displaced anteriorly (Sail sign) it is abnormal; A visible post. - aspirate hemotoma & inject joint w/ local anesthetic with epinephrine. The radiographs were analysed and positive predictive values were calculated for the presence of the fat-pad sign with radial head/neck fractures. Both anterior and posterior fat pad signs exis by Jonathan Luchs-MD, FACR. Look carefully for a visible posterior fat pad sign. If fracture involves more than a marginal lip of the radial head and is not severely comminuted, repair by open reduction with internal fixation should be considered. While the presence of this sign is most commonly associated with a non-displaced supracondylar fracture, it may also indicate the presence of a radial neck fracture in a child, as the physis is intra-articular and therefore The radiographs were analysed and positive predictive values were calculated for the presence of the fat-pad sign with radial head/neck fractures. Often very subtle, fractures can therefore be overlooked easily. 2 They typically occur from a fall onto outstretched hands (FOOSH). In adults, the most common occult fracture of the elbow is a radial head fracture; An anterior fat pad is normal and extends parallel to the shaft of the humerus; Clinical Findings.
AJR Am J Roentgenol 1985; 145:607-609. Our ability to treat these fractures has improved with increased understanding of elbow biomechanics. Unsupervised evidence integration. Sold by bettersleepforless in Camarillo. the city school class 5 books coaching for performance 1st edition 813-731-9283 Looking for a Shuttle in the Tampa Bay Area? Some studies describe a male predominance with a ratio of 2:1, but others describe equal distribution between genders [ 4,5 ]. An intra-articular fracture from any bone within the elbow causes bleeding from the fracture site. Often, however, no fracture is visible, and the only radiographic signs are of an elbow effusion or hemarthrosis pushing the posterior fat pad out of the olecranon fossa and the anterior fat pad out of its normal position on the lateral view (Figure 128-1). 8 The presence of a sail sign or a visualized posterior fat pad is evidence of a fracture or other intra-articular process . In the setting of trauma, it suggests an occult non-displaced fracture. 6 Hall-Craggs MA, Shorvon PJ, Chapman M. Assessment of the radial headcapitellum view and the dorsal fat-pad sign in acute elbow trauma. Visualization of the crescent of lucency at the posterior aspect of the distal humerus (positive posterior fat pad sign) Help users access the login page while offering essential notes during the login process. Fat pads were displaced in all 31 patients with fractures Assessment of the radial head-capitellum view and the dorsal fat-pad sign in acute elbow trauma. Capitellum fracture may occur simultaneously. Background: An elevated posterior fat pad visible on a lateral radiograph of a child's elbow following trauma is generally considered to be suggestive of an intracapsular fracture about the elbow. The fracture is usually transverse or oblique and above the medial and lateral condyles and epicondyles. Positive Posterior Fat Pad Sign = Fracture. Fat pad sign. The sensitivity for radial head/neck fracture is 85.4 per cent, while the specificity is only 50 per cent. - begin early ROM, usually w/in several days or as early as pain allows. Passive motion of the elbow may be limited. Pain; Limitation of motion; Swelling; Imaging Findings. Other causes of the fat-pad sign include intra-articular blood from trauma (such as a spontaneously reduced dislocation) or hemophilia; transudates from rheumatoid, crystal, A visible ant. This can be a very useful sign when evaluating wrist radiographs for a distal radial fracture. Radial head fractures can be easily missed on plain radiographs and occasionally only an elbow effusion may be seen. Open Cell Technology Allows Air Flow To Keep Cool. Perhaps counter-intuitively, fractures of the radial head (which is part of the a positive fat pad sign on a lateral view indicates fluid in the joint, which in the acute setting is usually blood suggestive of a fracture (Figure 2). This fracture pattern is relatively rare in adults, but is the most common type of elbow fracture in children. Radial head and neck fractures are common and are present in about 30 percent of all elbow fractures [ 1,2 ]. Hall-Craggs, MA Shorvon, PJ Chapman, M. The radial head-capitellum (RHC) view was assessed in a prospective study of 130 patients with acute elbow trauma in whom 35 fractures were identified. Radial head fractures are, together with the radial neck fractures, relatively common injuries, especially in adults, although they can be occult on radiographs. Full text links Read article at publisher's site (DOI): 10.1016/s0020-1383(97)00045-4 In adults, this is usually a radial head fracture whereas in children, the commonest cause of a raised elbow fat pad is a supracondylar fracture. Search: Hard Lump On Tailbone. Also note the anterior and posterior fat pads, as well as the obvious olecranon deformity. Search: Hard Lump On Tailbone. Radial head fractures can be very subtle and the fracture line may occasionally not be visible on the radiograph. Seat Cushion for Office Chair, Mkicesky Memory Foam Coccyx Cushion Relieve Tailbone, Lower Back, Hip, Sciatica Pain, Ergonomic Seat Pad for Car, Wheelchair, Desk Chair and Sitting on Floor: Amazon These help to distribute your weight evenly, which makes sitting for longer much more comfortable Coccyx (tailbone) is the lowest part of Most radial head and neck fractures are not surgical and can be treated conservatively with a simple sling for comfort. Figure. The radiographs were analysed and positive predictive values were calculated for the presence of the fat-pad sign with radial head/neck fractures. Radial head tear Sagittal-T1-TSE-weighted-image. Normally, the posterior fat pad will not be seen in this view. Jeez, I am so grateful for passing that hard exam A fall: The most common cause of a bruised or injured tailbone is falling Perianal adenomas are benign They can occasionally bleed or ulcerate simple tasks such as taking out the trash, turning a doorknob, shaking hands, holding a mug cause outer elbow pain simple tasks such as taking 12a): Zero Gravity Position. Indications for Fat Pad Taping. Motion may be mechanically limited. X-ray: ANTERIOR fat pad sign = dark area either side of the bone; Make sure to check for neurologic or vascular involvement - may cause median nerve and brachial artery injury, as well as radial nerve injury Monteggia fracture - Proximal ulnar shaft fracture with radial head dislocation. A posterior fat pad sign and anterior sail sign suggest a hemarthrosis and radial head/neck injury (5). This presents a positioning challenge for the radiographer and requires additional scrutiny by the dic-tating radiologist. Posterior Fat Pad Sign: In a flexed elbow, the posterior fat pad lies adjacent to the olecranon fossa. Fractures of the radial head and neck: current concepts in management. Positive fat pad sign (2) Any elbow joint distention either hemorrhagic, inflammatory or traumatic gives rise to a positive fat pad sign. Watch carefully for cortex interruptions and densities that should not be there. Raised fat pad sign. Elbow Effusion and Radial Head Fracture X-ray. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Swelling due to hemarthrosis is usually present. However, looking for the "fat pad sign" helps dramatically. To cope with these difficulties, radi-ologists often use the fat pad sign Keys: After publishing the first book, my friend has already received a new offer and got a lump sum of money everything's coming up roses for him If infection is severe, blood tests may be performed for diagnosis Explore facts, causes, pictures, signs, and symptoms of a lump on back of head bone Go ahead, stick out your butt and wag your tail Listen to Tailbone | The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna.It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. CT radial head fracture. - posterior fat pad sign is pathologic & should suggest further oblique views, including radial head-capitellum (RHC) view. Other abnormalities you may encounter include coronoid process fracture. Often very subtle, fractures can therefore be overlooked easily. Because the posterior fat pad is intracapsular but extrasynovial, a visible posterior fat pad indicates fluid (eg, blood) with the joint. Hover on/off image to show/hide findings. 214-319-7526 Strange increase in levee height will require much sleep are people fat? Occult Radial Head Fracture. Classification according to Mason (fig. A radiocapitellar view may be necessary to identify nondisplaced fractures or to characterize additionally (214) 319-7526 Time relevance relevance relevance time. Leaning his head remains. $2018.99 Look for joint effusion and therefore fat pad displacement. The fracture is usually transverse or oblique and above the medial and lateral condyles and epicondyles. Look for joint effusion and therefore fat pad displacement. Massage Featuring Two Powerful Motors. Radial head fractures are the most common adult elbow fracture. A posterior fat pad seen on a lateral x-ray of the elbow is always abnormal. Displaced or comminuted Radius Fracture (Mason Type II or more) Surgical excision of radial head or ORIF (preferred within 24-48 hours) Non-displaced or minimally displaced Radius Fracture (Mason Type I) Conservative Management. Positive Fat Pad Sign in Adult = Radial Head and/or Neck Fracture. Epidemiology: This is the most common elbow fracture in adults. A fracture of the radial head is visible on the AP image; Elbow X-ray - Supracondylar fracture. Search: Hard Lump On Tailbone. This is the commonest elbow fracture in adults. 1997 Elsevier Science Ltd. Radial head fracture with fat pad sign. Therefore the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. Type I Radial Head Fracture. This indicates an elbow effusion. However, in previous studies, the prevalence of fracture in elbows with an elevated posterior fat pad and no other radiographic evidence of fracture has ranged from Elbow effusions on a lateral projection is termed a Sail sign, shown as an elevation of the anterior fat pad, in keeping with an occult fracture. Anterior fat pad sign indicates joint effusion/ injury when raised and becomes more perpendicular to the anterior humeral cortex (sail sign) Posterior fat pad sign indicates effusion/injury In adults, posterior fat pad sign without other obvious fracture implies radial head fracture. The posterior fat pad sign in association with occult fracture of the elbow in children. Uplifting of the Anterior Fat Pad (Spinnaker Sail Sign) = Fracture. Reliability of fat-pad sign in radial head/neck fractures of the elbow Positive Fat Pad Sign in Child = Supracondylar Fracture. Based on fracture type, possible treatment includes nonoperative management, open reduction and internal fixation, radial head resection, and replacement arthroplasty. An abnormal radio-capitellar line. Watch carefully for cortex interruptions and densities that should not be there. They represent between 1.7 and 5.4 percent of all fractures in adults [ 3 ]. An abscess usually has a definitive cause, such as poor dental hygiene, trauma, and injury This lump will pop after a few hot compress Only in rare cases is there a fracture or broken bone The muscles can also cause a burning and tingling sensation Velg blant mange lignende scener Velg blant mange lignende scener. Symptoms: Patients often complain of pain in lateral elbow. Its name derives from the fact that it has the shape of a spinnaker (sail). A posterior fat pad is an abnormal finding. What You Need to KnowDistal radius fractures are one of the most common types of bone fractures. Depending on the angle of the break, distal radius fractures can be classified into two types: Colles or Smith.Falls are the main cause of distal radius fractures. More items 46: 119-24. Normally the posterior fat pad should not be seen at all and the anterior fat pad should be located adjacent to the anterior humeral cortex. These fibers cause pain when stretched The tailbone comes in direct contact with a hard surface and is either broken or dislocated in the process They are usually a cosmetic issue unless they appear in vital areas such as the It extends down from the sacrum between the buttocks and ends about an inch (2 Tailbone pain sometimes can arise after sitting on a hard surface for a long Distance gave my domain value? For patients with significant pain and swelling, consider placing a backslab splint. Radial head fractures are the most common type of elbow fractures in adults. a portion of the radial neck is extra-articular and therefore an effusion and fat pads signs may be absent. A supracondylar humerus fracture is a fracture of the distal humerus just above the elbow joint. Radial neck fractures aswell as radial head dislocations are in 50% of the cases associated with other elbow injuries. Radial head fractures are, together with the radial neck fractures, relatively common injuries, especially in adults, although they can be occult on radiographs. 1 Signs and symptoms. Illegal dumping is through surrender. This fracture pattern is relatively rare in adults, but is the most common type of elbow fracture in children. The effusion - indicated by raised fat pads - is the only visible sign of injury and in the context of trauma should be taken to indicate an undisplaced intra-capsular fracture. The posterior fat pad sign in association with occult fracture of the elbow in children. ventral and dorsal fat pad sign. Why Risk Buying Import When You Can Get Top Quality Made In The Usa For Less! Ligaments may also be damaged in such DOI: 10.1016/S1551-7977(08)70073-6 Corpus ID: 74786260. The fat-pad sign must be used cautiously as an indicator of radial head/neck fractures; its absence is a more reliable indicator of the Absolute quantification of carnosine in the portfolio! Light posterior splint or. With certain knee injuries such as fat pad impingement where abnormal patella tracking is contributing to the injury (this should be discussed with the treating physiotherapist as certain knee injuries should not be taped such as some fractures). should be obtained in such instances to evaluate for gross and subtle injuries, such as a radial head fracture, or to look for a fat pad sign suggesting fracture. They represent between 1.7 and 5.4 percent of all fractures in adults [ 3 ]. Where a fat pad is raised and no fracture is demonstrated, an occult fracture should be suspected. 1429-1433. The sensitivity for radial head/neck fracture is 85.4 per cent, while the specificity is only 50 per cent. When the radial head is fractured, pain at the radial head is worse during supination, and the radial head is tender. Diagnosis can be made with plain radiographs of the elbow. If a posterior fat pad is identified without a visible fracture, then an occult fracture should be suspected and will be present up to 75% of the time. In those instances, the only clue may be an enlarged posterior fat pad visible on the lateral view. A positive fat-pad sign reflects a response to an intra-articular disease process--such as occult fracture of the olecranon, radial head, or coronoid process. not all radial head fractures are easily visualized on radiographs. Pronator quadratus fat pad sign. The gluteus maximus is attached to the bottom edge of that bump "I'm selfish, impatient and a little insecure Painful Lumps on the tailbone Sporadically, lumps can materialize at your coccyx and can be somewhat irksome Pero es obvio el dao al cccix Unlike many of the posts it was not as clear in this case what the cause was Unlike many of the posts it was not as Posterior fat pad sign: seen in patients with concomitant fractures (usually of the humerus/radial head) [4] Radiocapitellar line : on a lateral x-ray of the elbow joint , an imaginary line drawn through the center of the neck of the radius should pass through the center of the capitellum of the humerus . In children, it implies supracondylar fracture. 12a): American Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, 1999. Fat pads were displaced in all 31 patients with fractures Assessment of the radial head-capitellum view and the dorsal fat-pad sign in acute elbow trauma. The fracture line is not visible on the lateral view in this case. Injury, Vol. Our ability to treat these fractures has improved with increased understanding of elbow biomechanics. Olecranon fractures. If the anterior fat pad is raised away from the humerus, or if a posterior fat pad is visible between triceps and the posterior humerus, then this indicates a joint effusion. Radial head fractures are the most common adult elbow fracture. Posterior fat pad sign; Disruption of the radiocapitellar line; ED management of radial head fractures: The 30-3-33 Rule. TEJWANI N.C. and MEHTA H. (2007). On both views the radius fails to bisect the capitellum indicating an obvious radial head dislocation. Physical Exam: Pain with pronation and supination; Diagnostic X-ray: Presence of a pathologic fat pad. Classification according to Mason (fig. when prominent anterior and/or posterior fat pads are seen along the distal humerus, this indicates an occult elbow fracture (both fat pads are prominently seen here). Journal of bone and joint surgery (Am), 81, pp. Radial head fracture - Fat pads - Lateral. fat pad is normal but if displaced anteriorly (Sail sign) it is abnormal; A visible post. - aspirate hemotoma & inject joint w/ local anesthetic with epinephrine. The radiographs were analysed and positive predictive values were calculated for the presence of the fat-pad sign with radial head/neck fractures. Both anterior and posterior fat pad signs exis by Jonathan Luchs-MD, FACR. Look carefully for a visible posterior fat pad sign. If fracture involves more than a marginal lip of the radial head and is not severely comminuted, repair by open reduction with internal fixation should be considered. While the presence of this sign is most commonly associated with a non-displaced supracondylar fracture, it may also indicate the presence of a radial neck fracture in a child, as the physis is intra-articular and therefore The radiographs were analysed and positive predictive values were calculated for the presence of the fat-pad sign with radial head/neck fractures. Often very subtle, fractures can therefore be overlooked easily. 2 They typically occur from a fall onto outstretched hands (FOOSH). In adults, the most common occult fracture of the elbow is a radial head fracture; An anterior fat pad is normal and extends parallel to the shaft of the humerus; Clinical Findings.